I write dark speculative fiction. #weirdfiction #darkfantasy #horrorfiction #scifi #postapocalypticfiction
Sunday, April 17, 2022
Sunday, April 3, 2022
Saturday, March 12, 2022
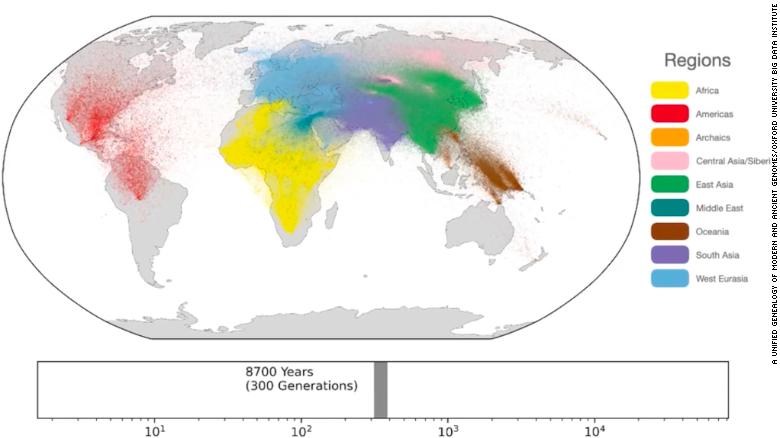
DNA REVEALS BIGGEST-EVER HUMAN FAMILY TREE
DNA reveals biggest-ever human family tree, dating back 100,000 years
An excerpt taken from the CNN article by Jack Guy, dated February 24, 2022
Friday, February 11, 2022
EVOLUTION OF EXPLORATION
EVOLUTION OF EXPLORATION -The first human explorers walked out of Africa, spreading to neighboring continents. Populations eventually reached Asia, and crossed a land bridge from Siberia to Alaska. We know this because there is a single woman, a common ancestor of all living humans. Everyone alive today carries a little piece of her in our mitochondria.
In Asia, humans living on the steppes tamed wild horses, eventually domesticating them sufficiently to ride on horseback. This took a considerable amount of nurturing, across multiple generations. Meanwhile, American migrations spread on foot, to Peru and beyond. Where the Inca used their vast road system for runners and llama caravans. To the north, Puebloan networks stretched from Teotihuacan to the Pacific. While the Mississippians lived in vast population centered around the river. Vikings from Europe first arrived on North America, by crossing the Atlantic in a rowboat. Much can be said about the devastation to native populations unleashed by later European migrations, a topic that will be deferred to a later article.
Regardless of the hemisphere humans inhabited, animal husbandry was integral to developing farms, and later, residential settlements. New frontiers meant new modes travel. Use of the horse drawn wagon made traveling overland, for greater distances, possible for the first time, more so than was feasible, compared to walking alone. Travel by water took many forms: from the first canoe, to rowboats, and sailboats. Greater scientific advancements brought an ability to travel further, often using astronomical charts to navigate the open oceans.
Engineers of the Industrial Revolution followed this feat with the steam powered engine - running ocean liners and locomotives all over the globe. The first automobile wasn’t far off, when most working class folks could still afford to buy a car. The time span between the first airplane flight and landing on the moon comes in at a mere 65 years. My "Evolution of Flight" article describes the period from the first hot air balloon to present.
The space race begins when the Soviets send out Sputnik 1, the first space probe. A slew of increasingly advanced probes since, have traveled as far as 486958 Arrokoth, a Kuiper belt object. It is the most distant object ever explored in our solar system at the time of this writing. The Hubble Space Telescope has been imaging galaxies as distant as 13 billion years away since 1990. The Space Shuttle program ran it’s course, and the International Space Station is aging. It will be re-orbited at some point in the future, to avoid an uncontrolled crash and burn. The Mars Ingenuity Helicopter made the first controlled flight on another world last year, in 2021.
Today, the James Webb Space Telescope orbits at Lagrange point 2, about 1 million miles away, on the dark side of the moon. It's first published image, a mosaic created over 25 hours, was taken in the early stages of aligning the telescope's 18 mirrors. There is a tangible possibility Webb can detect the signature of life on distant planets far afield in the Milky Way. With discoveries of water ice on both Mars and the Moon, there will certainly be more surface missions, and most likely, new settlements. A new age of exploration in human history has begin, all over again.
https://www.chadschimke.com/2022/02/evolution-of-exploration.html
https://www.chadschimke.com/2017/02/evolution-of-sound.html
https://www.chadschimke.com/2018/09/the-evolution-of-text.html
https://www.chadschimke.com/2017/09/evolution-of-images.html
https://www.chadschimke.com/2017/08/the-evolution-of-flight.html
https://www.chadschimke.com/2017/04/evolution-of-computing.html
Sunday, January 9, 2022
JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE
JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE - The James Webb Space Telescope pictured, as it propels away
from Earth’s upper atmosphere - headed into deep space. The image was captured on
12-24-21 by cameras on board the discarded upper stage. En route, a terrifying
number of complicated deployment procedures will be performed, by the most advanced
telescope every built, traveling to a preprogrammed Lagrange point. All
this will be done autonomously by onboard AI, since the telescope will be too far
away from Earth for instantaneous communication. Hopefully amazing photos taken of our planetary neighbors will soon be
forthcoming.
Saturday, September 22, 2018
EVOLUTION OF TEXT
https://www.chadschimke.com/2017/02/evolution-of-sound.html
https://www.chadschimke.com/2018/09/the-evolution-of-text.html
https://www.chadschimke.com/2017/09/evolution-of-images.html
https://www.chadschimke.com/2017/08/the-evolution-of-flight.html
https://www.chadschimke.com/2017/04/evolution-of-computing.html